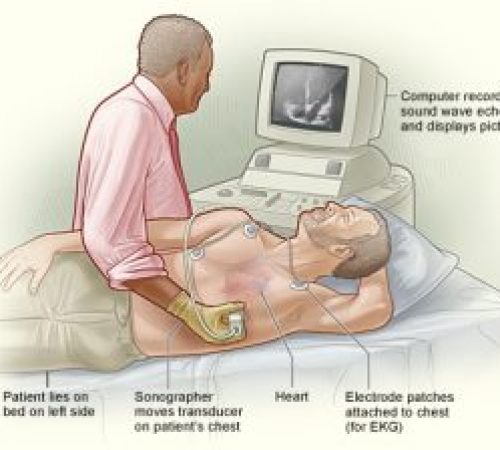
Echocardiography – It uses sound waves to create images of the heart. The images determine the size of the heart, strength of the heart muscles, presence of heart diseases, and heart valve malfunctions. The images of the heart are shown on the large screen monitor that allows the doctor and the patient to view during examination.
Why do I need an echo test?
Your doctor may use an echo test to look at your heart’s structure and check how well your heart is working.
This test may be needed if…
* You have a heart murmur.
* You’ve had a heart attack.
* You have unexplained chest pains.
* You’ve had rheumatic fever.
* You have a congenital heart defect.

How is it done?
Echo tests are done by trained sonographers. You
may have your test done in your doctor’s office, an
emergency room, an operating room, a hospital clinic or a hospital room.
* You’ll lie on a bed on your left side or back.
* The sonographer will put special jelly on a probe and move it over your chest area.
* Ultra-high-frequency sound waves will pick up images of your heart and valves. No X-rays will be used.
* Your heart’s movements can be seen on a video screen.
* A videotape or a photograph can be made of the pictures.
* You can sometimes watch during the test.
* It usually takes one hour.
* It’s painless and has no side effects.
* Sometimes the probe needs to be closer to your heart to give clearer pictures. You may need a special test called transesophageal echocardiography (TEE).
* As you swallow, a cardiologist will gently pass a tube with a probe on the end of it down your throat and into the esophagus. (This is the tube connecting your mouth to your stomach.)
